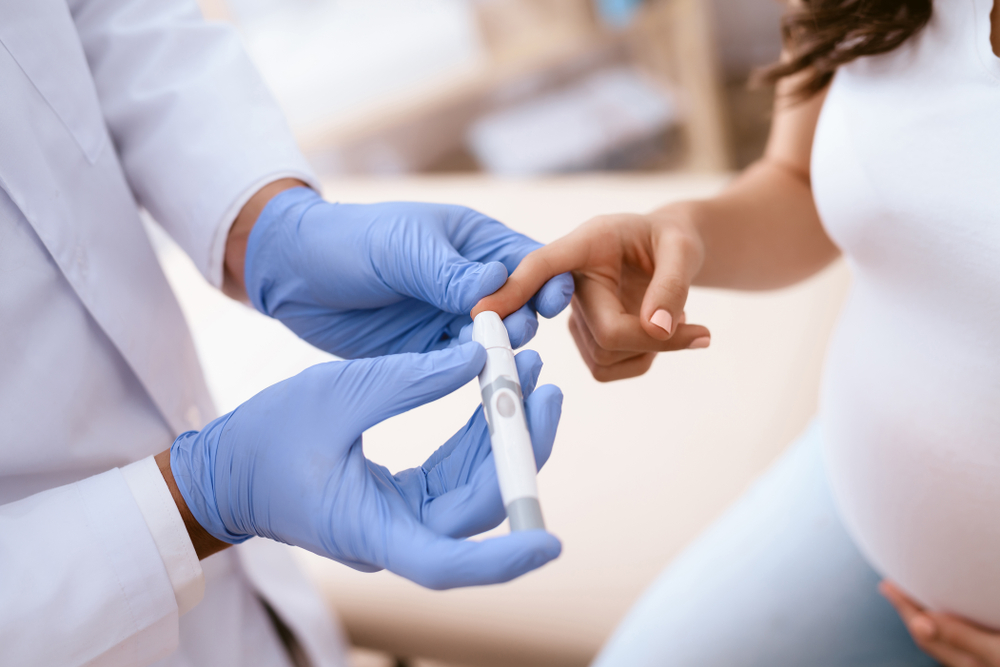
Genetic screening is a medical procedure that involves the examination of a person's DNA to identify changes or alterations that can potentially lead to genetic disorders. These tests offer valuable insights into an individual’s genetic makeup and the potential risks their baby may inherit. Being a fairly modern practice, it has revolutionized the field of medicine by enabling the early detection of various genetic disorders.
The process of genetic screening involves a series of tests carried out during pregnancy, especially during the prenatal stage. These tests help identify any potential genetic disorders that could affect the baby. The information gathered from these tests can provide crucial insights for parents and health care providers.
The Importance of Prenatal Genetic Screening
Prenatal genetic screening holds a significant place in modern healthcare, especially in the field of obstetrics and gynecology. It provides an early indication of various genetic disorders that an unborn baby might be at risk of developing.
As a future parent, you might be curious about your baby's health and well-being. Genetic screening can provide you with a sense of relief and assurance by confirming that your baby is not at risk of any severe genetic disorders.
Additionally, genetic screening is not just about identifying potential risks. It's also about understanding your genetic makeup and how it could potentially impact your baby. Knowing your genetic health can empower you to take proactive steps towards ensuring the health and well-being of your child.
What to Expect During the First Trimester
The first trimester marks the initial stages of your pregnancy, a period that is critical for the development of your baby. During this stage, there are genetic screening tests done between 10-13 weeks of pregnancy. These tests primarily aim to identify chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome or physical defects of the heart, abdominal wall, and skeleton.
One of the common genetic screening tests during the first trimester is the combined test. This test includes a blood test and an ultrasound, which measures the fluid at the back of the fetus’s neck. The results from these tests, combined with the mother's age, provide an estimate of the baby's risk of having certain chromosomal disorders.
What to Expect During the Second Trimester
As you move into your second trimester, blood will be drawn between 15-22 weeks of pregnancy. During the first 18-22 weeks of pregnancy, an ultrasound will be performed to identify physical defects in the brain and spine, facial features, abdomen, heart, and limbs.
The Benefits of Prenatal Genetic Screening
The benefits of prenatal genetic screening extend beyond the identification of potential genetic disorders. These tests provide a sense of security and allow parents to fully prepare for the arrival of their baby. They can also provide early indications of health issues that could affect the baby's life, allowing for effective treatment or management of the condition during pregnancy or after birth.
Being Well Informed with Genetic Screening
The choice to have a prenatal genetic screening is a personal one that should not be taken lightly. It's essential to discuss these tests with your healthcare provider to fully understand the benefits, risks, and implications. If you decide this option is right for you, it will provide valuable insights into your baby's health. It allows for the early detection of potential genetic disorders, enabling parents and healthcare providers to prepare and manage any risks effectively.
For more information on prenatal genetic screening, visit Partners in Obstetrics & Women’s Health at our office in New Lenox, Illinois. We provide expertise in the field of Obstetrics and Gynecology to give you the best possible care. Please call 815-240-0554 to schedule an appointment.